 What is Delayed Cord Clamping
What is Delayed Cord ClampingWhat's the lap cord and it's safe? If you are waiting for a child, you are likely to be learning about the many medical interventions that often take part in childbirth and delivery. Some of these, like epidurals, could be your choice. Others, like an emergency Caesarean, could be medically necessary. A practice you might have heard of is the fixing of late laces. The delayed closure means that the umbilical cord is not immediately held after birth. Instead, it's between one and three minutes after birth. Currently, most United States hospitals practice the early (immediate) cord fixation. This means cutting the umbilical cord. Before the mid-1950s, it was customary to wait one to five minutes before cutting the cord. Around this time, the number of births in hospitals began to increase. Research does not link specific benefits to a delay in fixing. It was believed that attachment early could prevent mothers from losing too much blood. Thus, healthcare providers began to cling before birth. In recent years, more research has drawn attention to how waiting to embrace the cord can benefit babies more. Lagment of fastening allows the blood to continue to flow from the placenta to the newborn baby after delivery. suggests that this blood can greatly benefit newborns, especially premature babies. Unless you're planning on, your baby's cord will hold and cut between a few seconds and a few minutes after delivery. The cord will be held in two places: near the navel of your baby and beyond the cord. The cord is cut between these clamps. If you have a partner with you, the doctor who delivers or midwife will usually ask if you want to cut the cord. The length of delay is not yet standardized. The medical opinion that the fixation is delayed when it occurs more than 30 seconds after birth. Waiting a minute allows your baby to receive about 80 milliliters (mL) of placenta blood. After three minutes, this increases to 100 mL. Until recently, most experts recommended keeping the baby in or near the placenta level (near the vagina) before setting the cord to increase blood flow to the baby. It was believed that raising the newborn above this level could allow the severity to pull the blood back to the placenta, reducing the blood flow to the baby. Because of that, some doctors and parents may feel reluctant to delay the spider if it also means a delay in skin-to-piel contact for the mother and baby. But a look at the effects of gravity on placenta blood flow in 391 babies born in three hospitals found no evidence to suggest that the position of the baby affected blood flow. If you want to delay the cord fixation but still keep your baby right after birth, you can do both. It is also safe for the baby to stop and start breastfeeding immediately. The newborn care routine, like weighing the baby, occurs once the cord is cut. Birth lotus vs. delay of cable fixing The birth of lotus is a delivery method where the cord is not immediately or short. In fact, it's not cut at all. Instead, the placenta is dry and falls naturally. This may take a few days to a week. The setting of delayed laces offers the greatest benefits for premature babies, but also benefits long-term babies and mothers. A delayed cord fixation linked to the increase and iron in long-term babies. This can reduce the risk of a baby for . One looked at 263 4-year-olds. In general, children whose strings were held three or more minutes after birth scored a little higher in an evaluation of fine motor skills and social skills that children whose strings were held 10 seconds or less after birth. Delayed clamping the need for blood transfusions and improve circulation in premature babies. It helps decrease the risk of bleeding in the brain and , an intestinal disease that affects almost premature babies. A delay in string fixing to a higher risk. But the benefits of delayed fixing can overcome this risk, provided that phototherapy treatment for jaundice is available. According to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), delayed clinging to the risk of , or excessive loss of maternal blood. Late cord fixing is possible if you have a Caesarean or vaginal delivery. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the delay in fixing is for caesarean births. The research that examines the effects of delayed fixation on multiple births is limited. A look at 449 women who have multiples did not find negative effects of fixing retarded laces for multiple births. This suggests that delayed fixing does not pose a greater risk if you are having twins. Two studies, one and one of , found delay in fixing to be safe and beneficial for premature twins. The immediate fixing of the rope is usually necessary if you are bleeding strongly after giving birth, if the baby is not breathing, or if another concern makes immediate medical attention necessary. The delay of one to three minutes before clinging. The delay of at least 30 to 60 seconds for healthy newborns. Standard practice in many US hospitals. is early fixing, so ask your midwife or doctor if they delay fixing. Including delayed attachment in your birth plan will allow your hospitalization team to know your preferences. Note that early setting of the cord may be necessary in some circumstances to keep you and your baby safe. Some parents choose after delivery to benefit medical research. This blood is a good source of stem cells. It can be stored and used to treat conditions like and. If you are thinking about cord banking and would like to delay cord fixing, there are some things to consider. The delay in laying the cord reduces the amount of blood that can be banking. It may not be possible to delay the cord fixing for more than 60 seconds and also the blood of the bank cord. A found that it was still possible to collect cord blood when clamping took place 30 to 60 seconds after birth. If you want to delay the cord fixation and also the blood of the bank cord, your care provider can give you more information about your options. Research suggests that fixing retarded laces is safe and beneficial to you and your baby. Both WHO and ACOG recommend delayed deferral. Your doctor or midwife may fasten and cut the cord immediately after delivery unless you request a delayed fixation. Mention your care team if you want to delay cable fixing and any other delivery preference you have before your scheduled date. Your doctor or midwife can help you decide the best option for your delivery. Last medical review on May 24, 2019 Read this next set of words
Umbilical cord delayed After birth This document has been withdrawn or is no longer available. Please contact the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists Resource Center by email or call for more information. ACOG's current clinical guide is available online at .Jump to: American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists 409 12th Street SW, Washington, DC 20024-2188 Copyright 2021. All rights reserved. Silence Please, Price ConfirmationBulk was not found for the item. Please try the recharge page. Price Member Price For additional amounts, please contact sales@acog.org or U.S. Call Free Call: (800) 762-2264 or (240) 547-2156 (Monday to Friday, 8:30 to 17:00)

Delayed Cord Clamping Benefits
Factors influencing placental transfusion with delayed cord clamping... | Download Scientific Diagram
Delayed Cord Clamping - PORTAL MyHEALTH
Delayed cord clamping. - ppt download![Why]()
Why "Delayed" Cord Clamping Should Be the Norm | Evolutionary Parenting | Where History And Science Meet Parenting
Delayed Cord Clamping & Cord Blood Banking in Singapore - Dr Pamela Tan
Cord Clamping 2
Find information about pregnancy, birth, breastfeeding, and tongue tie: Whether local to Bakersfield and Visalia, or online, there is something for parents and professionals alike here
A campaign re-born: physiological transition of the newborn with optimal cord clamping | All4Maternity
Delayed Cord Clamping: Benefits, Risks, and Recommendations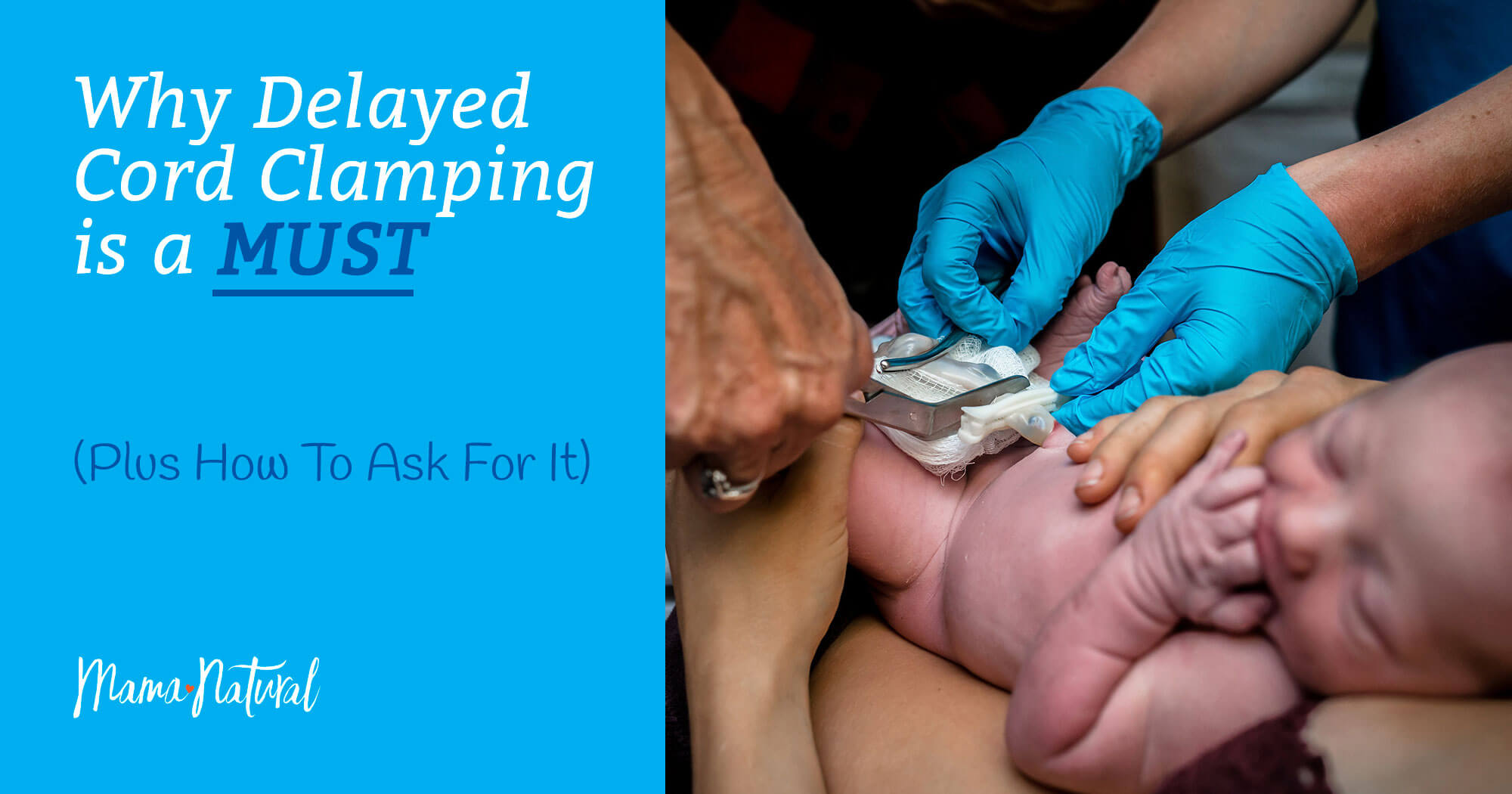
Why Delayed Cord Clamping Is a MUST (Plus How to Ask for It)
SMFM Consult--Delayed Umbilical Cord Clamping
Delayed Cord Clamping or Cord Milking | Latest news for Doctors, Nurses and Pharmacists | Obstetrics & Gynaecology![Full text] Delayed umbilical cord clamping after childbirth: potential benefits t | PHMT Full text] Delayed umbilical cord clamping after childbirth: potential benefits t | PHMT](https://www.dovepress.com/cr_data/article_fulltext/s51000/51867/img/Table2.jpg)
Full text] Delayed umbilical cord clamping after childbirth: potential benefits t | PHMT
Delayed cord clamping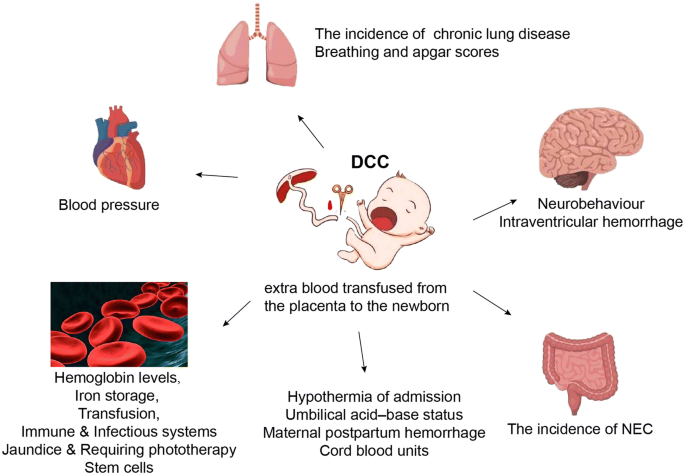
Early versus delayed umbilical cord clamping on maternal and neonatal outcomes | SpringerLink
Delayed Umbilical Cord Clamping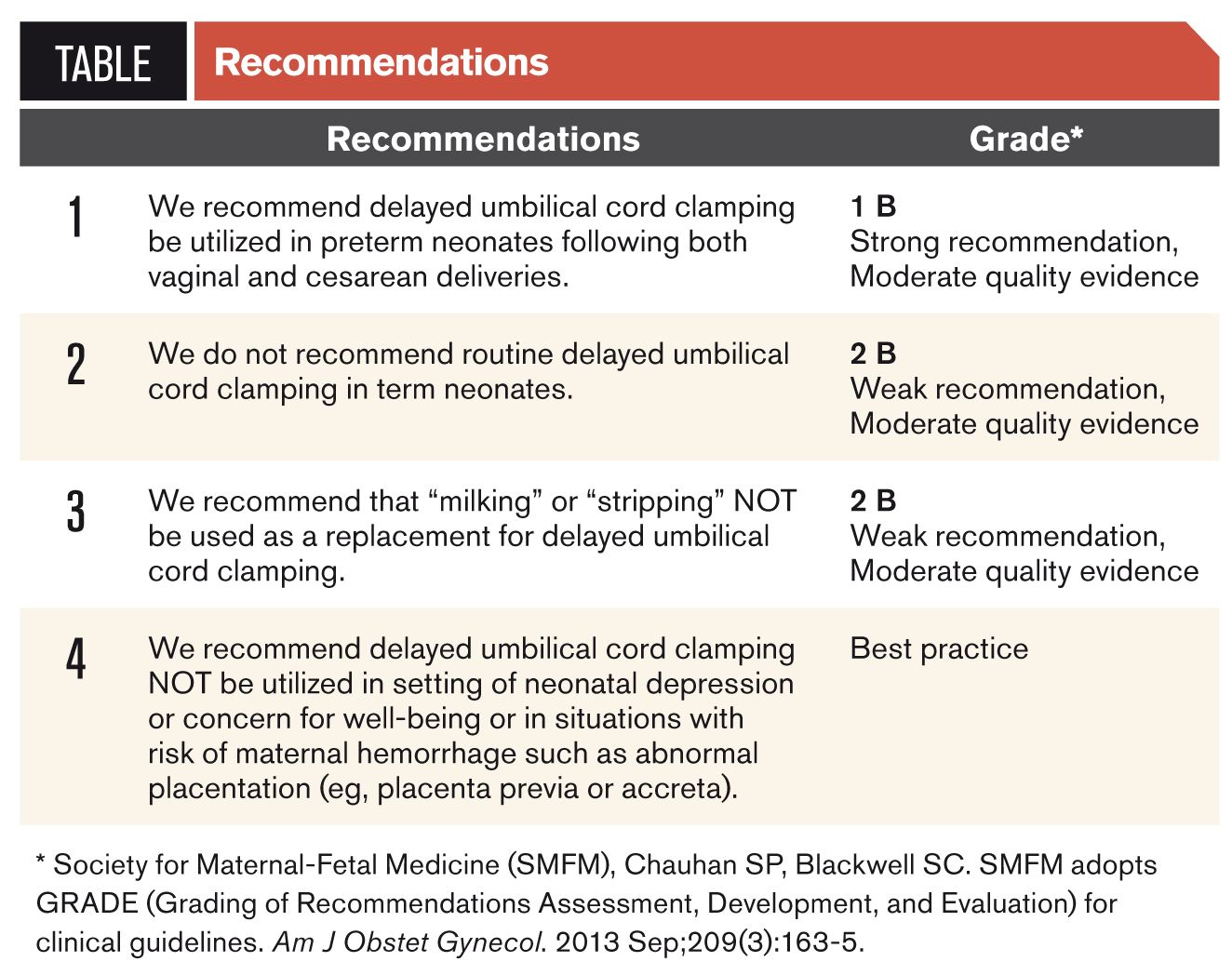
SMFM Consult--Delayed Umbilical Cord Clamping
Delayed Cord Clamping - Benefits and Risks
Benefits, Risks and Common Myths of Delayed Cord Clamping | Delayed cord clamping, Cord clamping, Baby supplies
delayed umbilical cord clamping | WomanPlace , Inc.![Full text] Delayed umbilical cord clamping after childbirth: potential benefits t | PHMT Full text] Delayed umbilical cord clamping after childbirth: potential benefits t | PHMT](https://www.dovepress.com/cr_data/article_fulltext/s51000/51867/img/Table3.jpg)
Full text] Delayed umbilical cord clamping after childbirth: potential benefits t | PHMT
Delayed cord clamping: much ado about nothing | The Skeptical OB
Delayed Cord Clamping in Newborns Born at Term at Risk for Resuscitation: A Feasibility Randomized Clinical Trial - The Journal of Pediatrics
Featured Review: Does delaying cord clamping or using cord milking at birth improve the health of babies born too early? | Cochrane
Here's why delayed cord clamping is the new normal | Pavilion for Women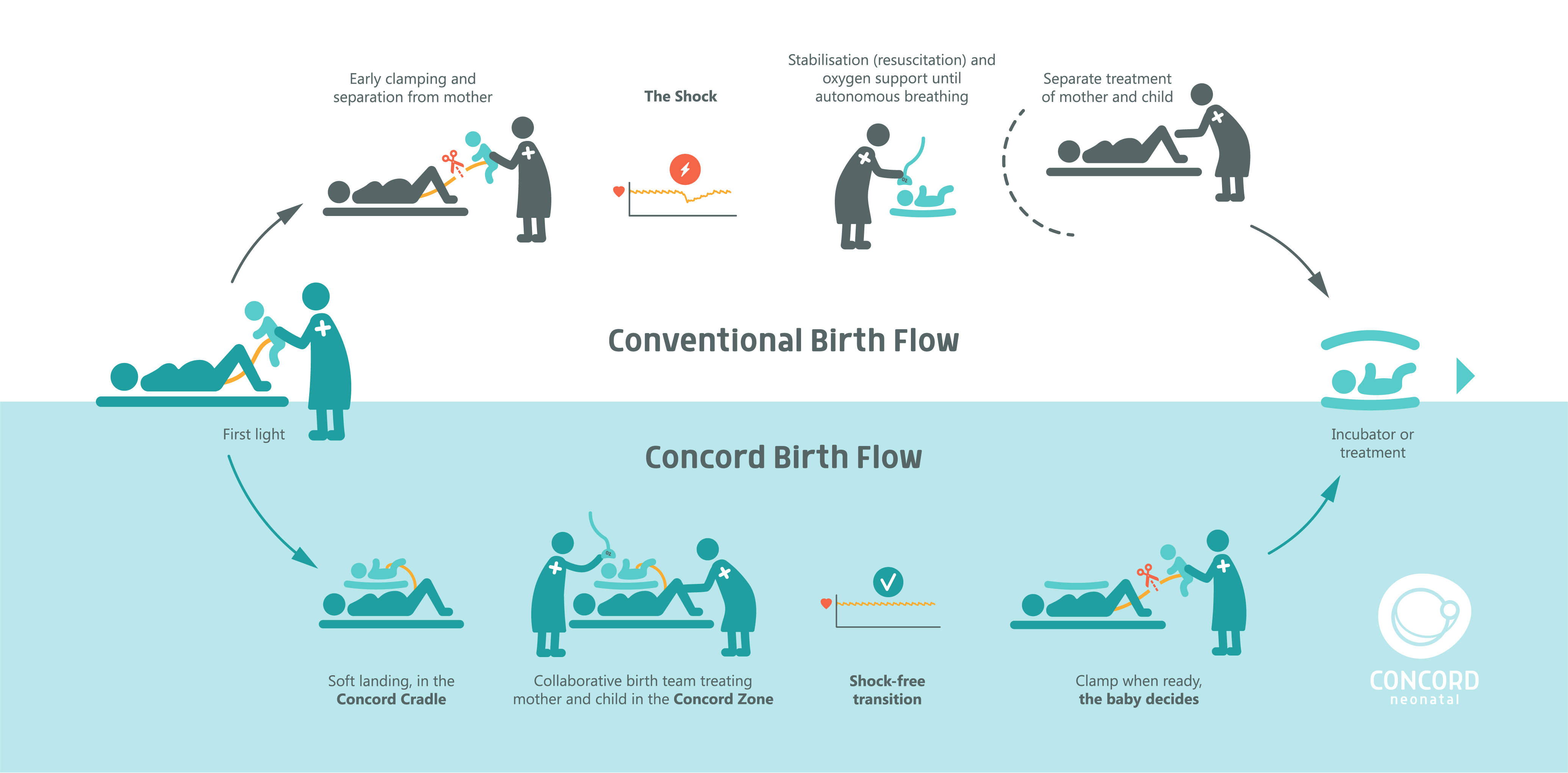
Delaying cord clamping – beneficial for ill or preterm born babies – EFCNI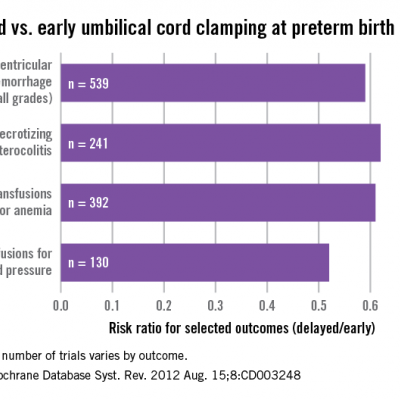
A step away from immediate umbilical cord clamping | MDedge ObGyn
Delayed cord clamping: Learn about it from an expert | theAsianparent
Advances in Neonatal Care - ppt download
Delayed Cord Clamping: Why Cord Blood Banking Hurts Your Baby - WeHaveKids - Family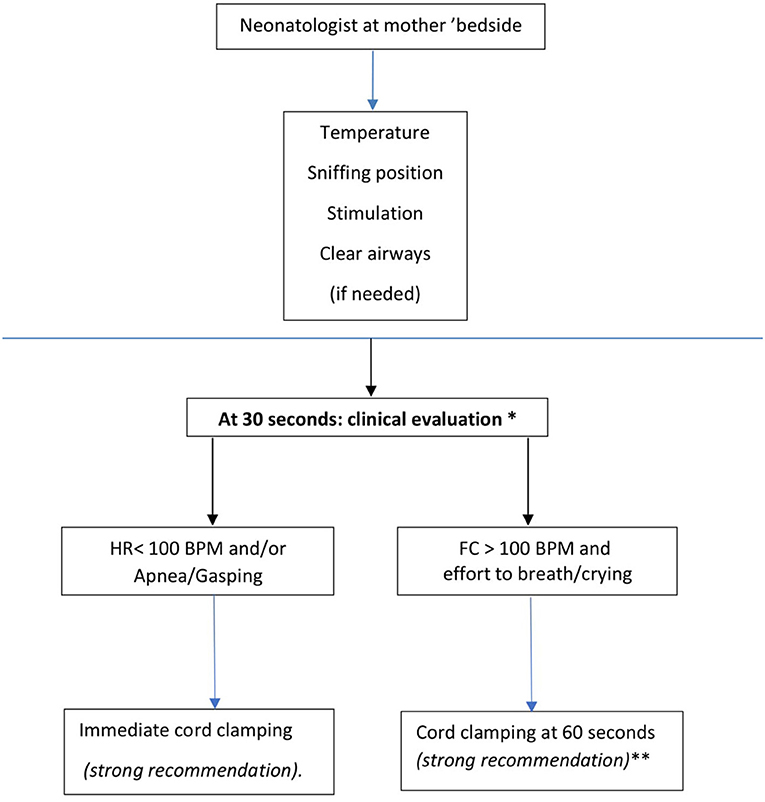
Frontiers | Italian Recommendations for Placental Transfusion Strategies | Pediatrics
Delayed cord clamping: Learn about it from an expert | theAsianparent
Delayed cord clamping in the very preterm | Neonatal Research
Umbilical cord blood utilization by vertical suspension alternative …
Delayed cord clamping was not associated with an increased risk of hyperbilirubinaemia on the day of birth or jaundice in the first 4 weeks - Rana - 2020 - Acta Paediatrica - Wiley Online Library
Optimizing placental transfusion by milking umbilical cord towards baby and its outcome – New Indian Journal of Pediatrics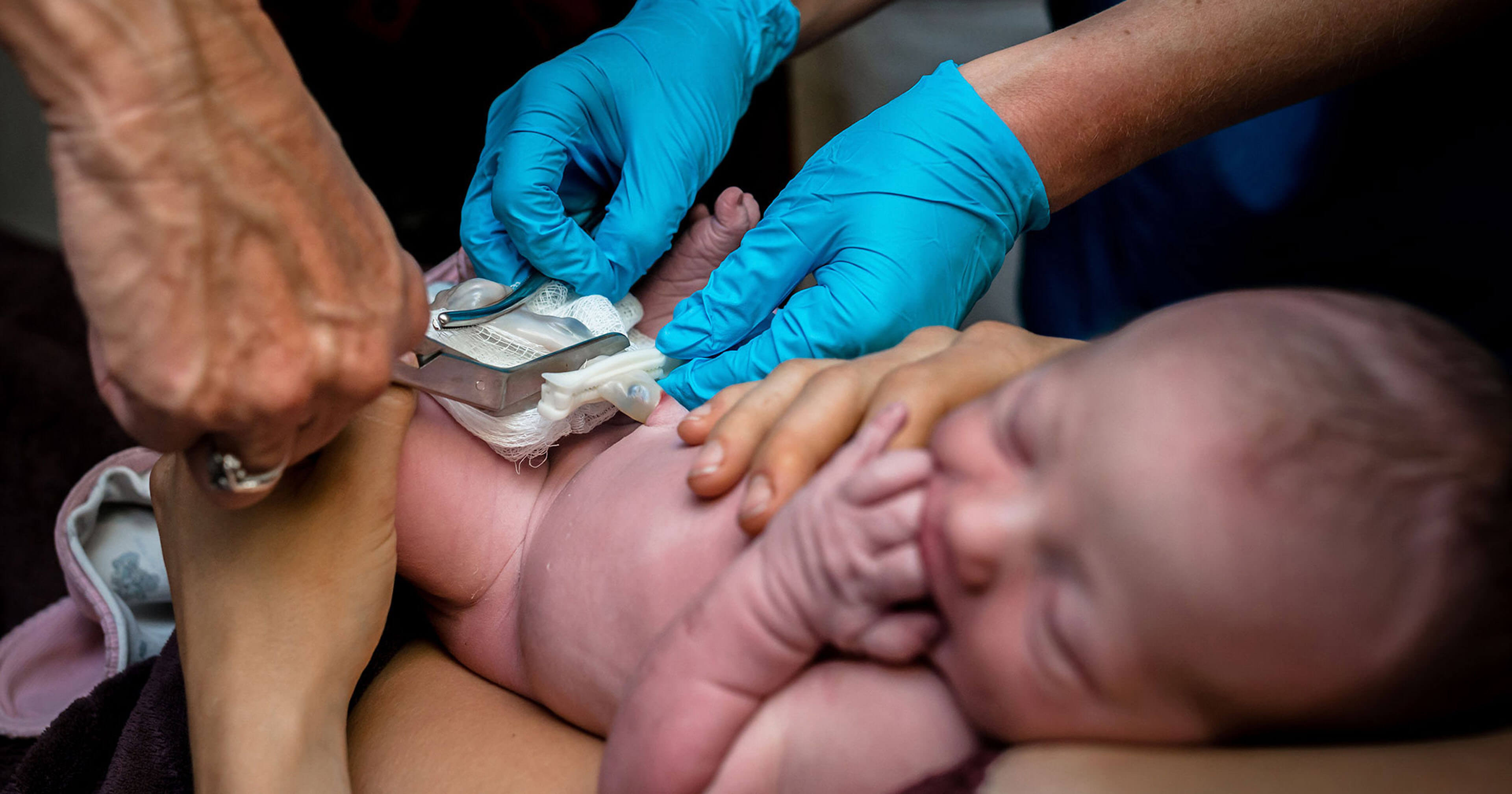
Why Delayed Cord Clamping Is a MUST (Plus How to Ask for It)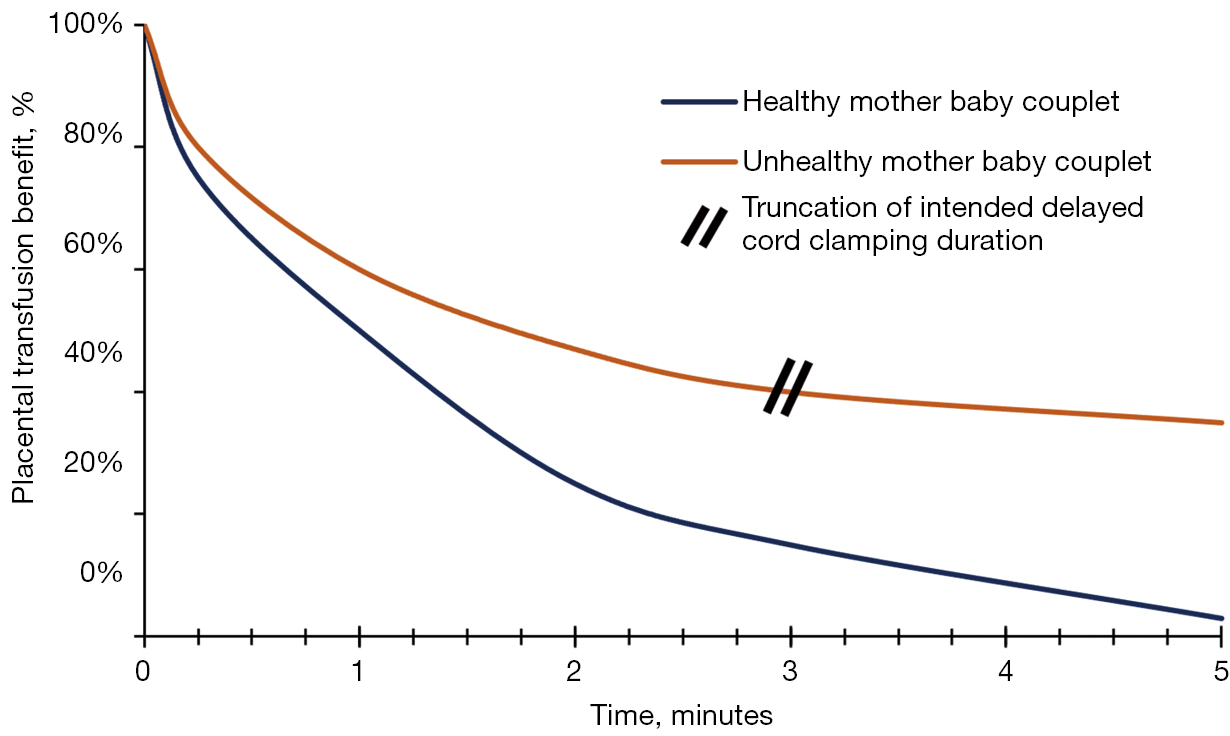
A narrative review of delaying cord clamping 2020—who, what, when, where, why and how? - Govindaswami - Pediatric Medicine
Pros and Cons of Delayed Cord Clamping - From the Cord Blood Experts











![Full text] Delayed umbilical cord clamping after childbirth: potential benefits t | PHMT Full text] Delayed umbilical cord clamping after childbirth: potential benefits t | PHMT](https://www.dovepress.com/cr_data/article_fulltext/s51000/51867/img/Table2.jpg)






![Full text] Delayed umbilical cord clamping after childbirth: potential benefits t | PHMT Full text] Delayed umbilical cord clamping after childbirth: potential benefits t | PHMT](https://www.dovepress.com/cr_data/article_fulltext/s51000/51867/img/Table3.jpg)
















Posting Komentar untuk "delayed cord clamping risks"